Working with Home Assistant (HA), and especially it’s yaml files, chances are that you have done a little edit that caused HA to stop working. Within the Graphical User Interface (GUI) there’s a possibility to verify configuration files, but I ‘ve seen it confirm my files, but yet the HA server didn’t come back up after I hit that restart button. Read on to find out about how to troubleshoot Home Assistant.
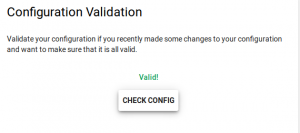
Home Assistant Configuration valid in GUI
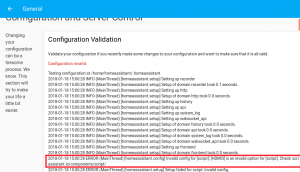
Home Assistant Configuration invalid in GUI
But what if you hadn’t checked your config before restarting and your GUI isn’t available?
Don’t panic
There’s still the command line (if you’ve enabled SSH Access that is).In this post I’ll show how to troubleshoot HA configuration files from the command line.
Requirements
- “Sudo” Type access to command line via ssh of your HA Server
- Basic Knowledge of editing text files in Linux with vi or nano
- Location of HA server files
Check whats’s wrong
To verify that the yaml files do not contain any typos (or tabs or missing spaces), we can use a built-in script in HA. Connect to your HA Server via SSH , and issue following command (sudo or as root):
/srv/homeassistant/bin/hass --script check_config -c /home/homeassistant/.homeassistant
Explanations:
- /srv/homeassistant/bin = install location of HA Server. Might be different from your setup, dependuing on how you installed HA.
- –script check_config = launch the check of the yaml files
- -c /home/homeassistant/.homeassistant = location of the HA config yaml files. Again, this might be different for your setup
If everything is valid, output looks like this:
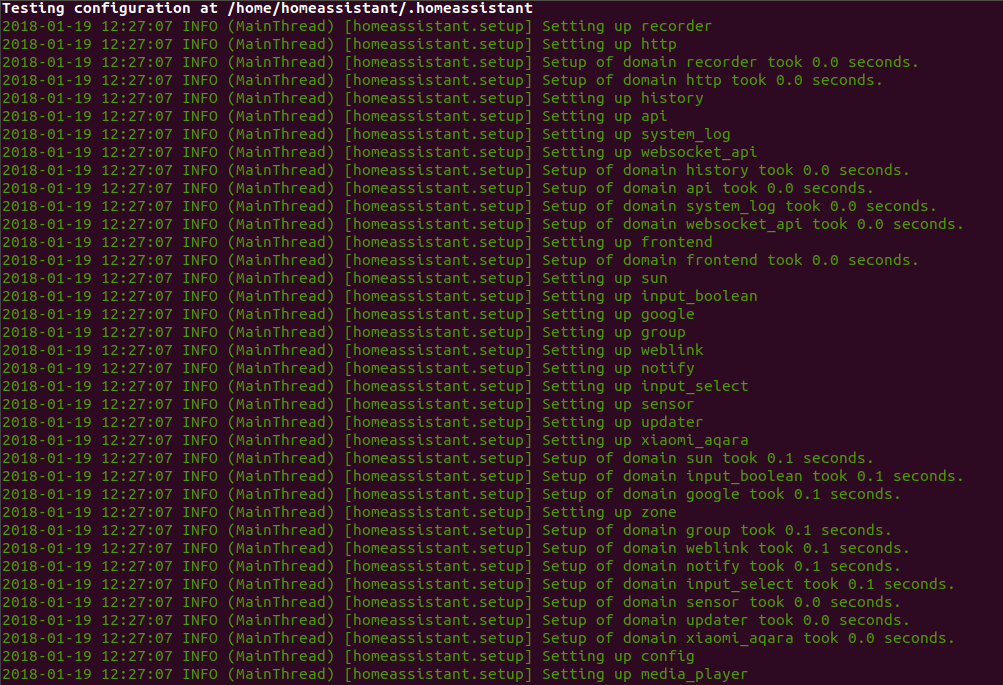
No errors detected
But since you’re reading this, it might contain an error:
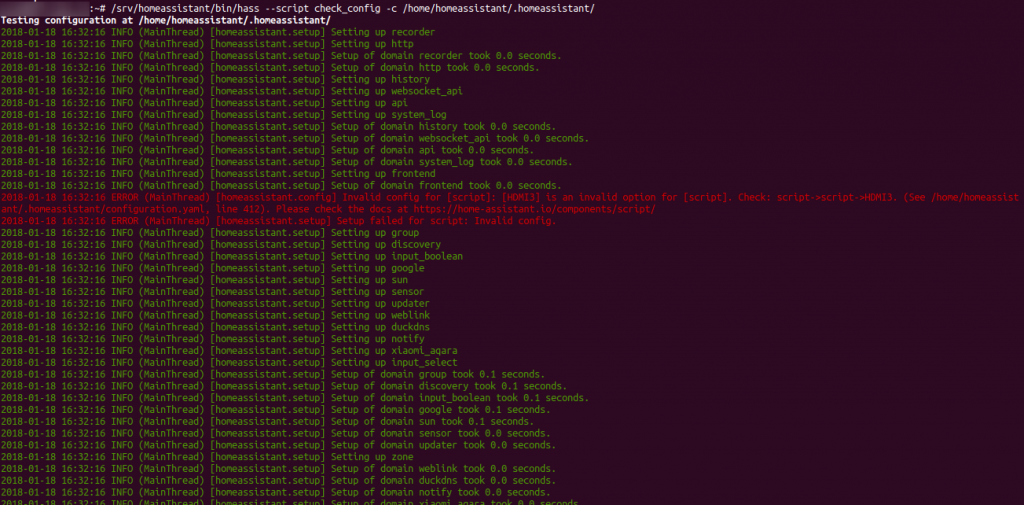
Error in scripts.yaml – Invalid Script Name provided
or like this:
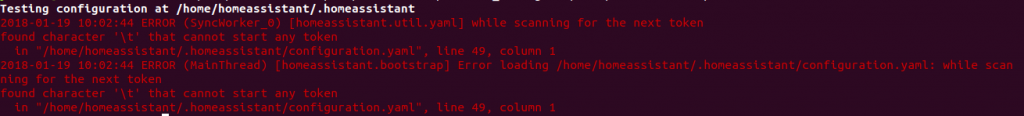
Error in configuration.yaml in line 49 – \t indicates that there is a “tab”, which is not allowed in a yaml file.
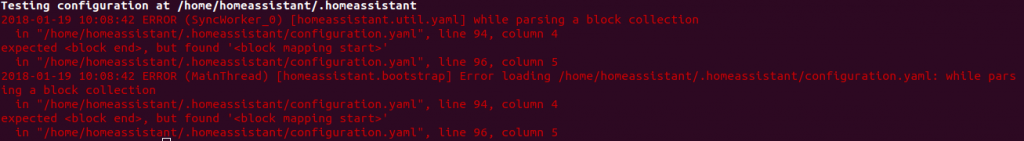
Error in configuration.yaml in line 94 – error parsing block collection indicates that there is an indentation problem.
Most likely you have a simple typo in one of your files. YAML uses a fixed indentation scheme to represent relationships between data layers. A single “space” too much (or not enough), or a “tab” will break your confgfig. Anyway, you now have the info which file ( and which line ) has to be edited.
Once the problem has been identified and corrected, simply restart HA with this command :
service home-assistant@homeassistant.service restart
Real-Time Logs
Another way to view what’s happening or what’s wrong with our system is by using a Operating Systen (OS) command to view logs. Like above, issue the following command as sudo or root:
journalctl -u home-assistant@homeassistant.service -f
Explanations:
- journalctl = view the systemlogs
- -u home-assistant@homeassistant.service = specify which account/service to display
- -f = keep continuously displaying new message
Quit with the Keyboard command CTRL+C .
You can also filter the output and look for specific events. I used following command to find the packets that my Broadlink RM Mini received from the various Remote Controls:
journalctl -u home-assistant@homeassistant.service -f | grep -i broadlink
- | grep -i broadlink = pipe the output to grep and print only lines that contain the case insensitive keyword broadlink.
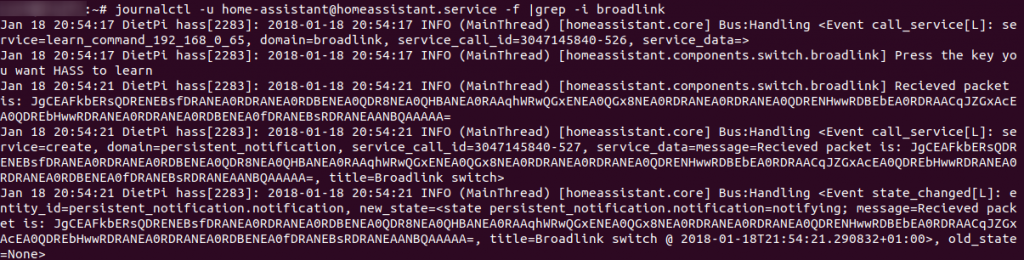
Filtered Display of journalctl, only broadlink messages are displayed
Thank your for reading this post. I hope it helps you to understand how to easily troubleshoot your Home Assistant Setup.
Feel free to leave a comment if you have any further questions or observations.
























Rezent Kommentare